A Holistic Approach to Chronic Pain Management: Exercise and the Biopsychosocial Model
When it comes to managing chronic pain, a one-size-fits-all solution is far from ideal. Chronic pain is a complex condition with physical, psychological, and social dimensions. To address these multifaceted aspects effectively, a biopsychosocial approach is crucial. In this blog post, we'll explore how exercise, when integrated into the biopsychosocial model, can be a powerful tool for managing chronic pain.
The Biopsychosocial Model
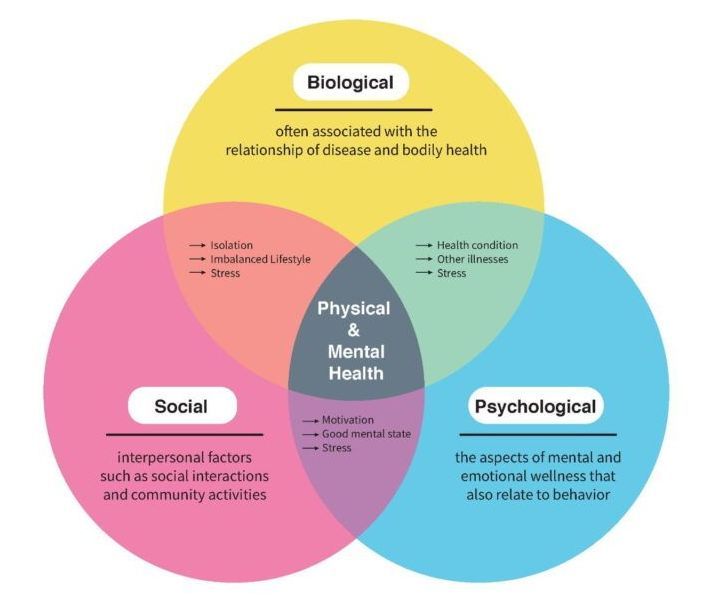
The biopsychosocial model of pain management acknowledges that chronic pain is not solely a result of physical issues. Instead, it recognises that biological, psychological, and social factors interact and contribute to the experience of pain. Here's how exercise can fit into each of these dimensions:
Biological Factors
Exercise is a key component in addressing the biological aspects of pain. When you engage in physical activity:
- Endorphin Release: Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers that affect the brain's perception of pain.
- Muscle Strengthening: Strengthening the muscles around the affected area can reduce strain on the joints and improve physical function.
- Improved Circulation: Regular exercise promotes better blood flow, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to damaged tissues, and aiding in their recovery.
Psychological Factors
Exercise can have a profound impact on the psychological aspects of pain:
- Mood Enhancement: The endorphins released during exercise can boost your mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression often associated with chronic pain.
- Coping Mechanism: Engaging in physical activity provides a positive coping mechanism and a sense of control over your pain, which can be empowering.
- Stress Reduction: Exercise can help reduce stress, which is known to exacerbate pain. Mindful exercises like yoga and tai chi combine physical activity with relaxation techniques to promote mental well-being.
Social Factors
Chronic pain can affect your social life and relationships, but exercise can help here as well:
- Social Support: Participating in group exercise or classes can provide a social support network, reducing feelings of isolation and improving motivation.
- Social Integration: Being part of an exercise community can help you feel connected to others, which is essential for mental and emotional well-being.
Incorporating the Biopsychosocial Approach
- Seek Guidance from an Exercise Physiologist: Collaborate with our team of allied health professionals, including exercise physiologists and exercise scientists, who are equipped to address every aspect of pain management.
- Personalised Exercise Plans: An Exercise physiologist can develop an exercise plan that considers your physical limitations, emotional well-being, and social support system.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Incorporate mindfulness and relaxation techniques into your exercise routine to address the psychological dimension of pain.
- Social Engagement: Consider joining exercise classes or groups to foster social connections while staying active.
Managing chronic pain through exercise is most effective when viewed through the biopsychosocial model. This holistic approach recognised the inter-connectedness of physical, psychological, and social factors in the experience of pain. By incorporating exercise tailored to your individual needs and working with a multidisciplinary healthcare team, you can address all dimensions of your chronic pain, improve your quality of life, and find relief on multiple fronts. Embracing the biopsychosocial model can lead to a more balanced and fulfilling approach to chronic pain management.
Book an initial consultation with one of our Exercise Physiologists TODAY